- IB
- Physics
IB Physics Data Booklet
RevisionDojo's IB Physics SL and HL Data Booklet is designed to give IB students a clear, exam-ready reference to every essential physics formula, constant, and equation you’ll need. Unlike generic physics resources, our booklet is directly aligned with the official IB Physics syllabus, ensuring that you practice with the exact data and formulas you'll have access to during your exams.
Whether you're revising mechanics, thermal physics, waves, fields, or quantum theory, our clean layout and topic-by-topic structure make it easy to locate the right information under exam pressure. For students aiming to maximize efficiency, this resource is the perfect companion to our IB Physics notes, question bank, and past papers, giving you a complete toolkit for IB Physics success.
Data Booklet
Mathematical equations

Uncertainties
| If: | then: |
|---|---|
| If: | then: |
| If: | then: |
Fundamental constants
| Quantity | Symbol | Approximate value |
|---|---|---|
| Acceleration of free fall | (Earth's surface) | |
| Gravitational constant | G | |
| Avogadro constant | ||
| Gas constant | 8.31 | |
| Boltzmann constant | ||
| Stefan-Boltzmann constant | ||
| Coulomb constant | k | |
| Permittivity of free space | ||
| Permeability of free space | ||
| Speed of light in vacuum | c | |
| Planck constant | ||
| Elementary charge | e | |
| Electron rest mass | ||
| Proton rest mass | ||
| Neutron rest mass | ||
| (Unified) atomic mass unit | u | |
| Solar constant | ||
| Fermi radius |
Metric (SI) multipliers
| Prefix | Abbreviation | Value |
|---|---|---|
Unit conversions
- 1 radian
- Temperature temperature
- 1 light year
- 1 parsec
- 1 astronomical unit
- 1 kilowatt-hour
Electrical circuit symbols
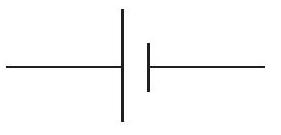
Cell
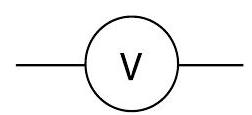
Voltmeter
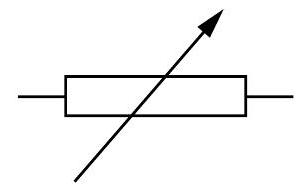
Variable resistor
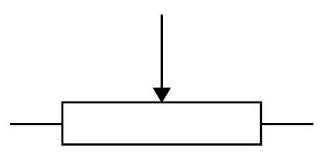
Potentiometer
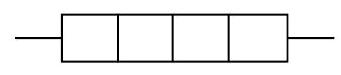
Heating element

Battery
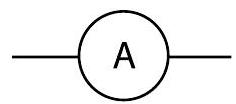
Ammeter

Light-dependent resistor (LDR)
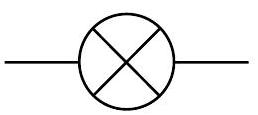
Lamp
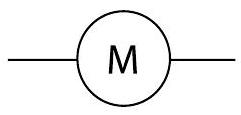
Motor

Switch
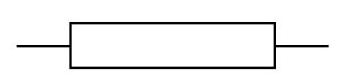
Resistor
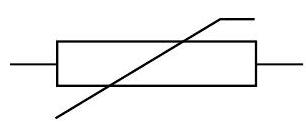
Thermistor
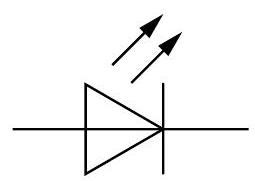
Light emitting diode (LED)
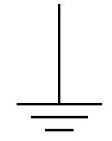
Earth (ground)
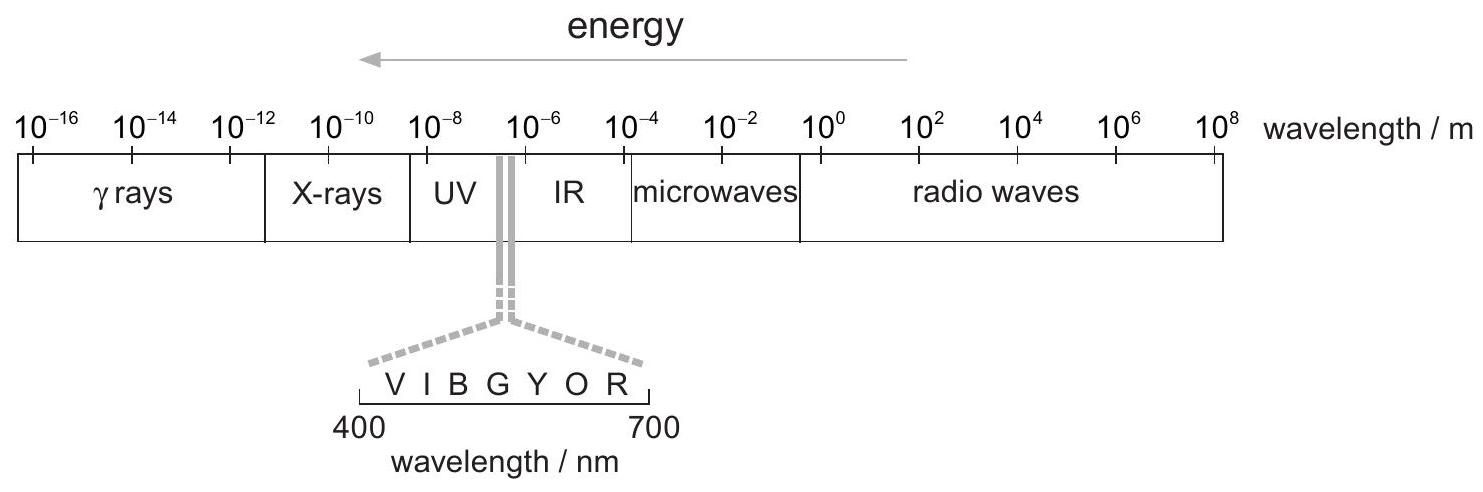
Electromagnetic spectrum
A. Space, time and motion
| Standard level and higher level | |
| A. 1 Kinematics | |
| A. 2 Forces and momentum | |
| A. 3 Work, energy and power | |
| Additional higher level | |
| A. 4 Rigid body mechanics | |
| A. 5 Galilean and special relativity |
B. The particulate nature of matter
| Standard level and higher level | |
| B. 1 Thermal energy transfers | |
| B. 2 Greenhouse effect | |
| B. 3 Gas laws | |
| B. 5 Current and circuits | |
| Series circuits | |
| Additional higher level | |
| B. 4 Thermodynamics |
C. Wave behaviour
| Standard level and higher level | |
| C. 1 Simple harmonic motion | |
| C. 2 Wave model | |
| C. 3 Wave phenomena | Constructive interference: path difference Destructive interference: path difference |
| C. 5 Doppler effect | |
| Additional higher level | |
| C. 1 Simple harmonic motion | |
| C. 3 Wave phenomena | |
| C. 5 Doppler effect | Moving source: Moving observer: |
D. Fields
| Standard level and higher level | |
| D.1 Gravitational fields | |
| D.2 Electric and magnetic fields | |
| D.3 Motion in electromagnetic fields | |
| Additional higher level | |
| D.1 Gravitational fields | |
| D.2 Electric and magnetic fields | |
| D.4 Induction | |
E. Nuclear and quantum physics
| Standard level and higher level | |
| E. 1 Structure of the atom | |
| E. 3 Radioactive decay | |
| E. 5 Fusion and stars | |
| Additional higher level | |
| E. 1 Structure of the atom | |
| E. 2 Quantum physics | |
| E. 3 Radioactive decay |

