- IB
- SL 3.5—Intersection of lines, equations of perpendicular bisectors
Practice SL 3.5—Intersection of lines, equations of perpendicular bisectors with authentic IB Mathematics Applications & Interpretation (AI) exam questions for both SL and HL students. This question bank mirrors Paper 1, 2, 3 structure, covering key topics like core principles, advanced applications, and practical problem-solving. Get instant solutions, detailed explanations, and build exam confidence with questions in the style of IB examiners.
The line joining the points and meets the - and -axes at the points and , respectively.
Find the equation of line and calculate the length of the segment .
The line through the point is perpendicular to the line . This new line intersects the -axis at point and the -axis at point .
Calculate the ratio .
The equations of the sides , , and of triangle are given as:
Find the coordinates of point . Then, determine the equation of the line through that is perpendicular to line . This line intersects the -axis at point and the -axis at point . Calculate the ratio .
The straight line passing through the points and intersects the line at the point .
Find the coordinates of .
Find the gradient of the line that passes through the points and .
Find the gradient of the line that passes through the points and .
A line passes through the point and has a gradient of .
Find the equation of the line in the form .
In a city park, three security cameras are positioned at points A(1,4), B(4,1), and C(7,6) to monitor different areas. To optimize coverage, the park administration wants to find the boundary line equidistant from cameras A and B and analyze its significance for park security.
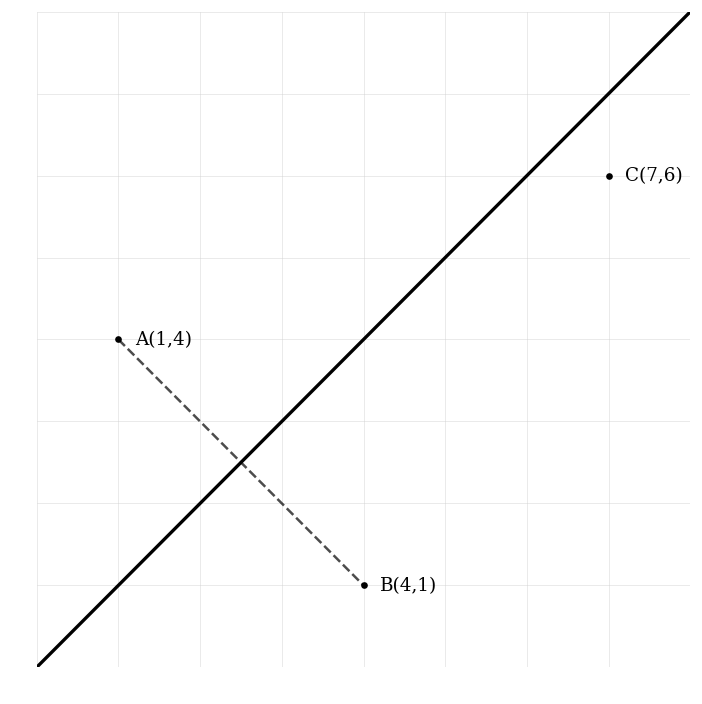
Find the midpoint of the line segment AB, which will help determine the location of equal distance between the two cameras.
Calculate the slope of the line segment AB to analyze the orientation of the cameras’ line of sight.
Determine the slope of the perpendicular bisector of AB, which would represent the line along which additional cameras could be placed for optimal coverage.
Write the equation of the perpendicular bisector in slope-intercept form () of the line segment connecting points A(1,4) and B(4,1).
Explain the geometric significance of the perpendicular bisector within the context of this park and how it relates to coverage optimization.
Calculate the perpendicular distance from the point to the line joining the points and .
Calculate the perpendicular distance from the point to the line joining the points and .
Consider the points and .
Determine the coordinates of the midpoint of the line segment joining and .
Let the points be and .
Show that the equation of the perpendicular bisector of segment is
Given that this perpendicular bisector passes through the point , find the value of .