- IB
- AHL 3.16—Tree and cycle algorithms, Chinese postman, travelling salesman
Practice AHL 3.16—Tree and cycle algorithms, Chinese postman, travelling salesman with authentic IB Mathematics Applications & Interpretation (AI) exam questions for both SL and HL students. This question bank mirrors Paper 1, 2, 3 structure, covering key topics like core principles, advanced applications, and practical problem-solving. Get instant solutions, detailed explanations, and build exam confidence with questions in the style of IB examiners.
A logistics manager must visit six warehouses ( P to U ) to inspect inventory, starting and returning to P . The travel times (in hours) are given in the table below.
| P | Q | R | S | T | U | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P | - | 5 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 15 |
| Q | 5 | - | 6 | 9 | 11 | 14 |
| R | 8 | 6 | - | 7 | 10 | 13 |
| S | 10 | 9 | 7 | - | 8 | 12 |
| T | 12 | 11 | 10 | 8 | - | 9 |
| U | 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 9 | - |
Use Kruskal's algorithm to find the minimum spanning tree, listing edges in order of selection.
Find a lower bound for the travelling salesman problem starting and returning to P.
Apply the nearest neighbour algorithm starting at P to find an upper bound.
Explain how deleting vertex Q could improve the lower bound.
A city maintenance crew must inspect all roads in a network represented by the weighted graph , where vertices represent intersections and edges represent roads with weights indicating distances in kilometers.
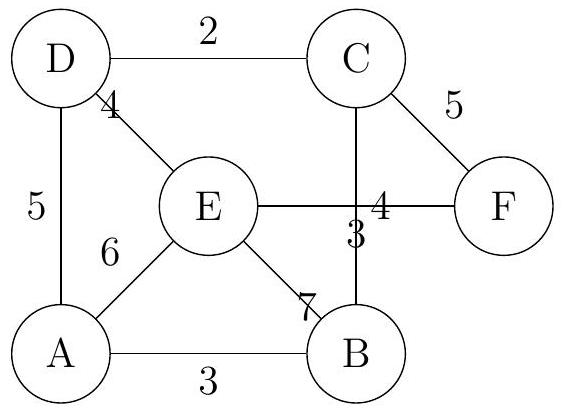
Verify that graph satisfies the handshaking lemma.
Determine whether graph has an Eulerian trail, giving a reason for your answer.
Use the Chinese Postman algorithm to find the minimum distance the crew must travel to inspect all roads, starting and ending at vertex A. Clearly show all stages of the algorithm.
If the crew can start at vertex A and end at vertex F , find the minimum distance they need to travel, explaining which edges should be repeated.
Based on the graph:
Using Kruskal's algorithm, determine the minimum spanning tree, and state its weight.
Using Prim's algorithm starting at vertex , determine the minimum spanning tree, and state its weight.
A communication network has vertices with the following adjacency matrix .
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
Compute the number of walks of length 3 from to .
Determine if the graph is connected and find its diameter.
A logistics company plans to visit six depots () in a region, with travel times in hours given in the distance matrix below.
| A | B | C | D | E | F | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | - | 3 | 5 | 7 | 9 | 11 |
| B | 3 | - | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 |
| C | 5 | 4 | - | 5 | 7 | 9 |
| D | 7 | 6 | 5 | - | 4 | 8 |
| E | 9 | 8 | 7 | 4 | - | 6 |
| F | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 6 | - |
Apply Kruskal's algorithm to find the minimum spanning tree, listing edges in order of selection and stating the total weight.
Find a lower bound for the travelling salesman problem using the deleted vertex method with vertex .
Use the deleted vertex method with vertex to find an improved lower bound.
Based on the graph:
Create the complete weighted adjacency matrix (including the shortest weighted connection between every two vertices).
Find the upper bound for the travelling salesman problem using vertex A.
Based on the graph:
Solve the Chinese Postman Problem for this graph.
Based on the graph:
Create an unweighted adjacency matrix for the graph.
Hence, identify the odd vertices.
Hence, find the solution to the Chinese Postman Problem.
The diagram below shows a network of roads in a small village with the weights indicating the distance of each road, in metres, and junctions indicated with letters.
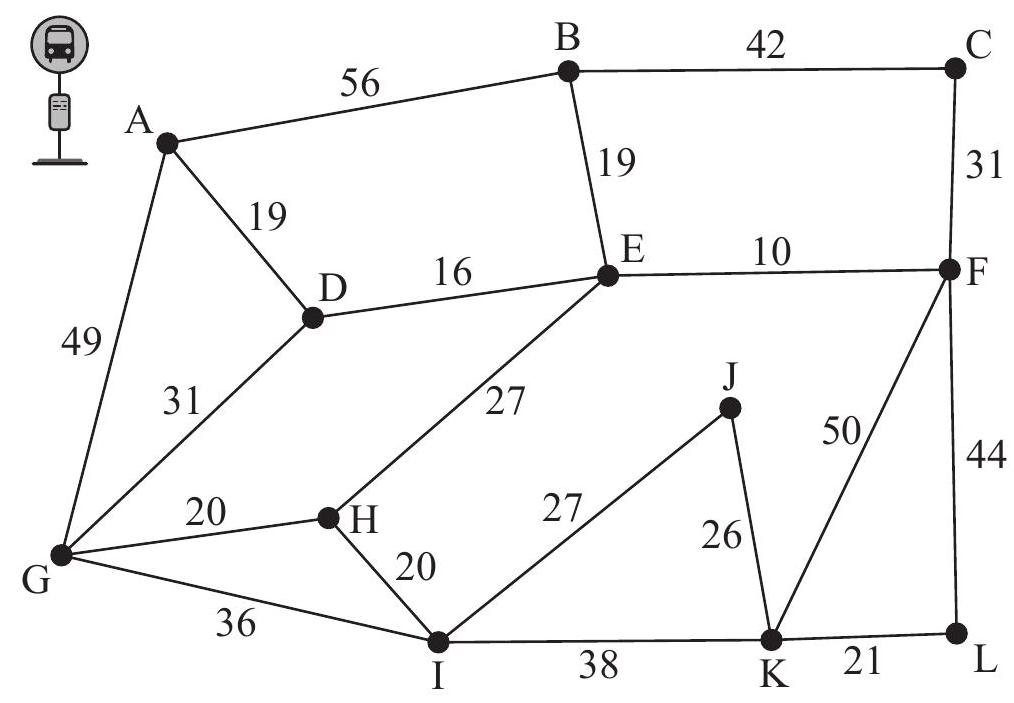 Musab is required to deliver leaflets to every house on each road. He wishes to minimize his total distance.
Musab is required to deliver leaflets to every house on each road. He wishes to minimize his total distance.
Musab starts and finishes from the village bus-stop at A. Determine the total distance Musab will need to walk.
Instead of having to catch the bus to the village, Musab's sister offers to drop him off at any junction and pick him up at any other junction of his choice. Explain which junctions Musab should choose as his starting and finishing points.
Consider a weighted graph with vertices and the following adjacency matrix representing edge weights.
| 0 | 3 | 5 | 2 | |
| 3 | 0 | 4 | 6 | |
| 5 | 4 | 0 | 3 | |
| 2 | 6 | 3 | 0 |
Use Kruskal's algorithm to find the minimum spanning tree of .
Verify if the graph has an Eulerian circuit or trail.