Practice AHL 3.14—Graph theory with authentic IB Mathematics Applications & Interpretation (AI) exam questions for both SL and HL students. This question bank mirrors Paper 1, 2, 3 structure, covering key topics like core principles, advanced applications, and practical problem-solving. Get instant solutions, detailed explanations, and build exam confidence with questions in the style of IB examiners.
A graph has the degree sequence:
Is this a valid simple graph? Justify using the Havel-Hakimi algorithm.
How many edges does the graph contain?
The position vector of a particle, , relative to a fixed origin at time is given by .
Find the velocity vector of .
Show that the acceleration vector of is never parallel to the position vector of .
Based on the graph:
Using Kruskal's algorithm, determine the minimum spanning tree, and state its weight.
Using Prim's algorithm starting at vertex , determine the minimum spanning tree, and state its weight.
A connected graph has 6 vertices.
Find the minimum number of edges in the graph.
A graph has an adjacency matrix . You are told that the entry .
What does this entry represent?
How can this information be used in analyzing graph connectivity?
Based on the graph:
Create the complete weighted adjacency matrix (including the shortest weighted connection between every two vertices).
Find the upper bound for the travelling salesman problem using vertex A.
Based on this graph:
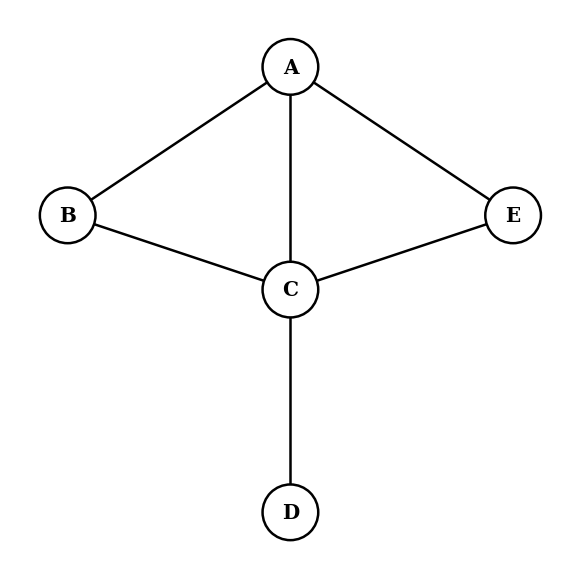
Write down the adjacency matrix for this graph.
Find a Hamiltonian path in this graph.
State the change that would be needed for a Hamiltonian cycle to be present.
Based on the graph:
Solve the Chinese Postman Problem for this graph.
Based on the graph:
Create an unweighted adjacency matrix for the graph.
Hence, identify the odd vertices.
Hence, find the solution to the Chinese Postman Problem.
The diagram below shows a network of roads in a small village with the weights indicating the distance of each road, in metres, and junctions indicated with letters.
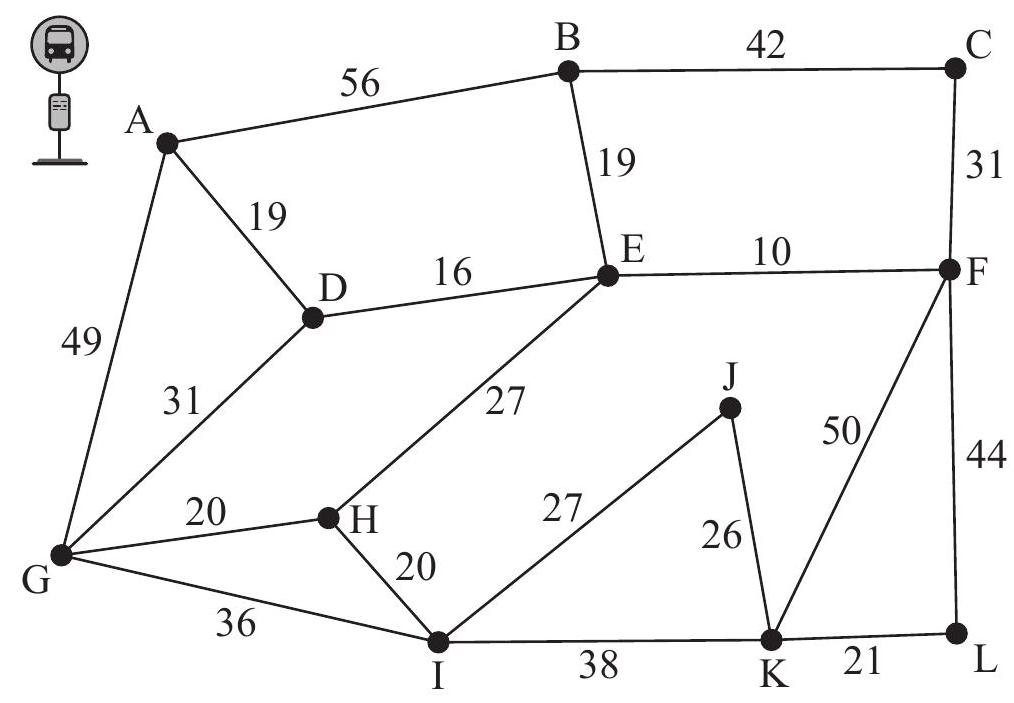 Musab is required to deliver leaflets to every house on each road. He wishes to minimize his total distance.
Musab is required to deliver leaflets to every house on each road. He wishes to minimize his total distance.
Musab starts and finishes from the village bus-stop at A. Determine the total distance Musab will need to walk.
Instead of having to catch the bus to the village, Musab's sister offers to drop him off at any junction and pick him up at any other junction of his choice. Explain which junctions Musab should choose as his starting and finishing points.