- IB
- SL 3.7—Circular functions, graphs, composites, transformations
Practice SL 3.7—Circular functions, graphs, composites, transformations with authentic IB Mathematics Analysis and Approaches (AA) exam questions for both SL and HL students. This question bank mirrors Paper 1, 2, 3 structure, covering key topics like functions and equations, calculus, complex numbers, sequences and series, and probability and statistics. Get instant solutions, detailed explanations, and build exam confidence with questions in the style of IB examiners.
Consider the function .
Find the amplitude of .
Determine the possible values of such that has a period of .
Given that , find the -coordinates of the maximum and minimum points of in the domain .
Consider the equation
Show that the equation may be written as
Factor the left-hand side to show that
Explain why implies , and hence deduce a quadratic inequality for .
Find all exact values of consistent with , and hence determine all exact values of in that satisfy the original equation.
Sketch the graphs of and for , indicating points of intersection that correspond to your solutions from part 4.
Let and , for . The graph of is shown on the diagram below. There is a maximum value at .
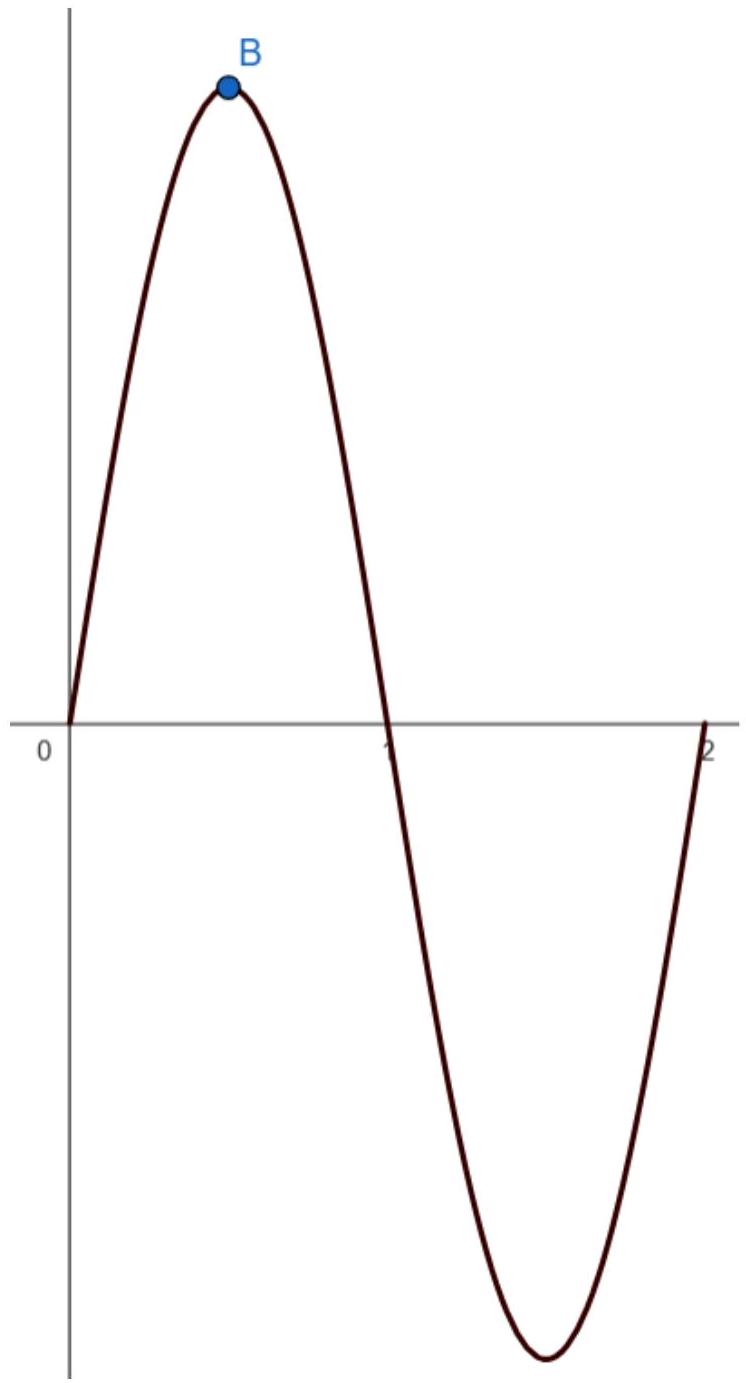
Find the value of .
On the same diagram, sketch the graph of .
Solve for .
The function is defined for .
State the amplitude and period of .
Determine the -intercepts of in the given interval, in exact form.
Find the coordinates of the first maximum point of .
Solve, for , the equation Give exact solutions.
Sketch one full period of , clearly indicating amplitude, period, and intercepts.
Consider the equation
Show that the equation may be written as
Express in terms of , and hence obtain a quadratic equation in .
Solve exactly for .
Determine all exact values of in the interval that satisfy the original equation.
Sketch the graphs of and for , indicating two approximate intersection points corresponding to your solutions from part 4.
Consider the equation
Show that the equation may be written as
Express in terms of , and hence obtain a quadratic equation in .
Solve exactly for .
Determine all exact values of in the given interval that satisfy the original equation.
Sketch the graphs of and for on the same axes, indicating approximate points of intersection corresponding to your algebraic solutions.
Analyze the transformations applied to the basic cosine function.
Describe the transformations applied to the function .
Sketch the graph of over the interval .
Consider the function .
Given the function , for what values of is the period ?
Now consider with a period of . Graph the function for and under the domain .
Hence, find the area of the region enclosed by the graphs.
The graph of is transformed into the graph of .
Find a sequence of simple geometric transformations that does this.
Sketch the function showing at least one complete period.
Sketch the function showing at least one complete period.