- IB
- SL 3.1—3d space, volume, angles, distance, midpoints
Practice SL 3.1—3d space, volume, angles, distance, midpoints with authentic IB Mathematics Analysis and Approaches (AA) exam questions for both SL and HL students. This question bank mirrors Paper 1, 2, 3 structure, covering key topics like functions and equations, calculus, complex numbers, sequences and series, and probability and statistics. Get instant solutions, detailed explanations, and build exam confidence with questions in the style of IB examiners.
Consider a triangle such that has coordinates has coordinates and has coordinates where
Let be the midpoint of the line segment .
Find, in terms of , a Cartesian equation of the plane containing this triangle.
Find, in terms of , the equation of the line which passes through and is perpendicular to the plane .
Consider a water tank in the shape of an inverted cone with a height of 10 metres and a base radius of 5 metres. Water is being pumped into the tank at a rate of 3 cubic metres per minute.
Find the rate at which the water level is rising when the water is 4 metres deep.
A research drone is tethered by two cables, and , attached to points and on level ground. The points and are 80 m apart. The drone is directly above the point on the ground. In the horizontal triangle , the angle at between the lines and is .
At a certain instant, the angle of elevation of the drone from is and from is .
Draw a fully-labelled 3-D diagram showing and all known angles.
Let the horizontal distances m and m. Show that
Using the cosine rule in triangle , show that
Use your results from part 2 and 3 to find the height of the drone above the ground. Give your answer to the nearest metre.
The drone then moves horizontally so that its projection traces out a circular path of radius 80 m centred at . Calculate the angle swept by in radians and the length of the arc of this path when the bearing of from changes from to .
The tension in each cable is proportional to its length. If the tension in is and in is , find the ratio at this instant.
A cylindrical tank that stores water has a height of and a volume of .
Find the radius of the base of the cylinder.
They would like to store the water in a cone instead. Find the height of a cone which has the same radius and the same volume as the cylinder.
A rescue helicopter hovers above a mountain valley. It is connected by two winch cables to huts and on level ground. The distance between the huts is . The helicopter is vertically above point , and in the horizontal triangle , .
The angle of elevation of the helicopter is from and from .
Sketch a fully-labelled 3-D diagram showing and all given angles.
Let m and m. Show that
Using the cosine rule in triangle , write down an equation relating and .
Use your results to find the height of the helicopter above the ground, correct to the nearest metre.
The point later moves horizontally around a circular path of radius centred at . Find the length of the arc, in metres and radians, when its bearing from changes from to .
If tensions are and , find .
A hot-air balloon is anchored by two ropes to points and on level ground. The distance is 75 m. The balloon is vertically above , and in the horizontal triangle .
The angles of elevation of the balloon are from and from .
Draw a fully-labelled 3-D diagram showing and all the given angles.
Let m and m. Show that
Using the cosine rule in triangle , write an equation relating and .
Find the height of the balloon, to the nearest metre.
The projection moves horizontally on a circle of radius centered at . Find the angle subtended by the arc in radians and the length of the arc in metres when the bearing of from changes from to .
If and , find .
The points and are given by and .
The plane is defined by the equation .
Find a vector equation of the line passing through the points and .
Find the coordinates of the point of intersection of the line with the plane .
Consider a cylinder with diameter , height and a fixed volume of . The total surface area of the cylinder, , is given by the expression , where is a constant.
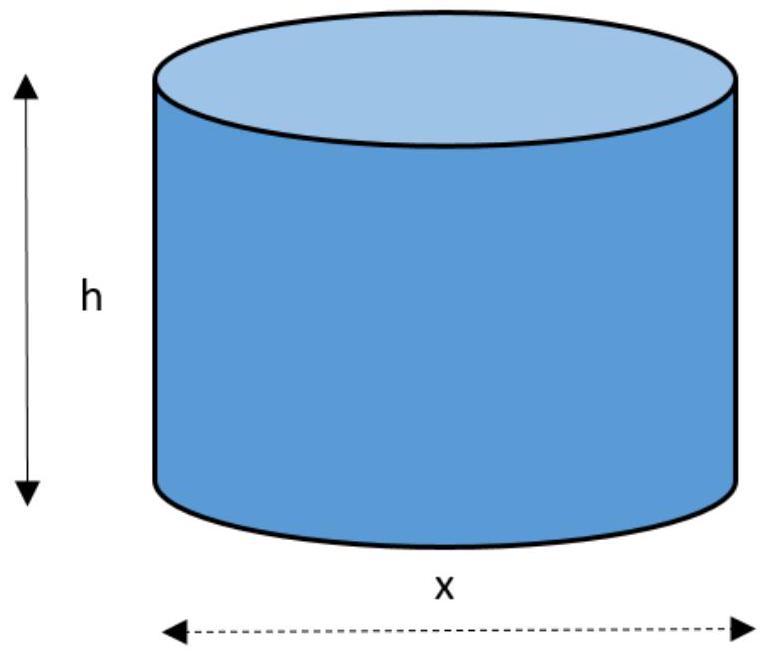
Find the value of .
Find the value of that minimizes the total surface area.
A mall is to be constructed with a concrete slab foundation. In order to fit this foundation, a rectangular section of earth measuring by is removed to a depth of . The removed earth is used to create a hemispherical structure in order to reduce waste.
Find the diameter of the hemispherical structure.
The architect decides to replace the hemispherical structure with a cylindrical structure of height . The maximum straight line distance available on the site is . Find the radius of the cylindrical structure and show that it is not suitable for the site.
Find the volume and surface area of a cylinder with radius and height . Give your answers in terms of .
Find the volume and surface area of a sphere with radius . Give your answers in terms of .