Practice B.1.3 Muscular function with authentic IB Sports, exercise and health science (SEHS) exam questions for both SL and HL students. This question bank mirrors Paper 1A, 1B, 2 structure, covering key topics like core principles, advanced applications, and practical problem-solving. Get instant solutions, detailed explanations, and build exam confidence with questions in the style of IB examiners.
Identify three types of movement possible at synovial joints.
State three anatomical terms used to describe body position.
Describe the role of tendons and ligaments in generating and controlling movement.
Explain how the structure of skeletal muscle enables force production.
Describe the function and application of third-class levers in sport.
Identify the two frontal plane movements.
State two functions of synovial fluid.
Describe how the sagittal plane relates to running mechanics.
Explain the relationship between ligaments and injury prevention.
Outline the differences between fast-twitch and slow-twitch muscle fibers.
Explain how understanding anatomical movements improves sports technique.
What is the main function of the structures labelled E and F in the motor neuron?
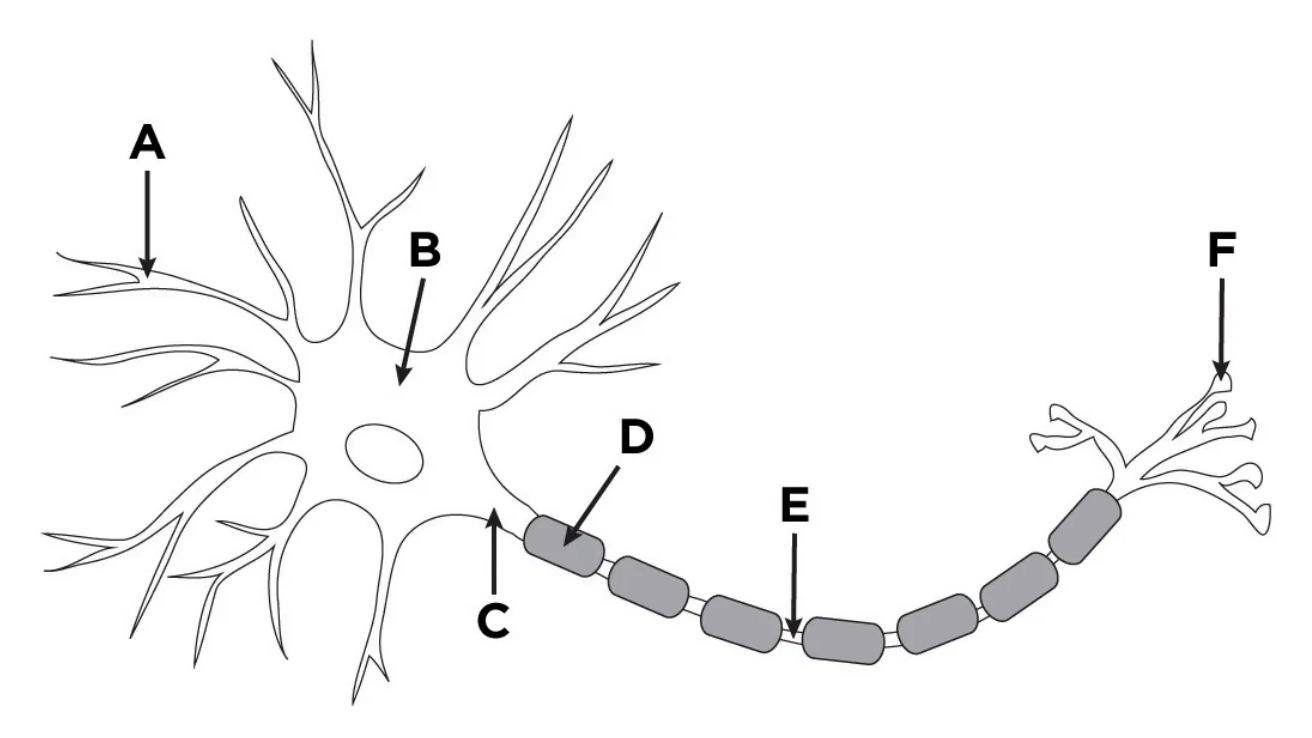
Which of the following correctly identifies the structure labeled D in the image?
Why are isometric contractions useful in rehabilitation exercises?
Which contraction type is responsible for maintaining posture during standing?
Holding a plank position is an example of which type of contraction?
What triggers the exposure of binding sites on actin during the sliding filament process?
Which protein filament has binding sites for myosin heads in the sliding filament theory?
Which type of contraction produces the greatest muscle damage and adaptation, such as in plyometric training?