Practice A.2 Forces and momentum with authentic IB Physics exam questions for both SL and HL students. This question bank mirrors Paper 1A, 1B, 2 structure, covering key topics like mechanics, thermodynamics, and waves. Get instant solutions, detailed explanations, and build exam confidence with questions in the style of IB examiners.
Two players are engaged in a game of table tennis. Player A strikes the ball at a height of 0.27 m above the table's surface, measured from the tabletop to the bottom of the ball. The ball's initial velocity is in the horizontal direction.
Assume that air resistance is negligible.
The ball bounces and then reaches a peak height of 0.19 m above the table with a horizontal speed of . The mass of the ball is 3.6 g.
Show that the time taken for the ball to reach the surface of the table is about 0.2 s.
Sketch, on the axes provided below, a graph showing the variation with time of the vertical component of velocity of the ball until it reaches the table surface. Take to be .
The net is stretched across the middle of the table. The table has a length of 4.84 m and the net has a height of 9.8 cm.
Show that the ball will go over the net.
Player B intercepts the ball at its highest point. Holding the paddle stationary in a vertical position, Player B makes contact with the ball for 0.010 s. Assume the collision is perfectly elastic.
Calculate the average force exerted by the ball on the paddle. State your answer to an appropriate number of significant figures.
Determine the kinetic energy of the ball immediately after the bounce.
A sledge carrying a box slides down a smooth snow slope, starting from rest at the top. The slope curves smoothly until it becomes horizontal, as shown.
Assume there is no friction between the sledge and the snow. Air resistance is negligible.
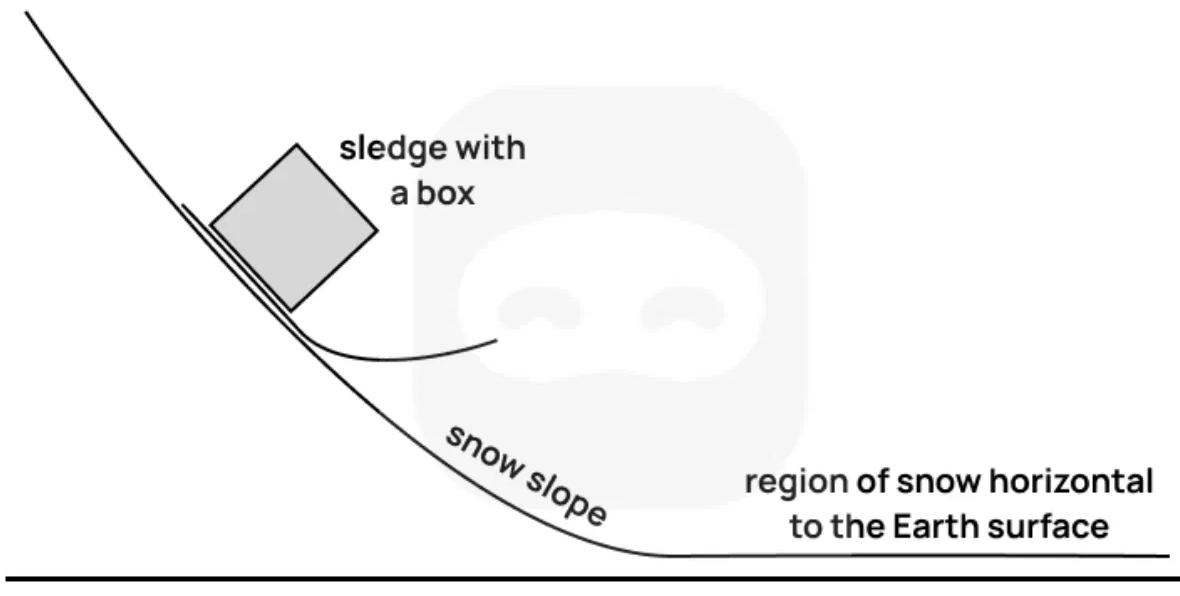
State the energy transformations taking place as the sledge descends the slope.
The sledge and box together have a mass .
At the top of the slope, the sledge is at a vertical height above the horizontal surface. Determine an expression for the speed of the sledge when it reaches the horizontal snow region.
Explain why the normal force exerted by the snow changes as the sledge moves down the curved part of the slope.
After reaching the horizontal region, the sledge travels a distance before coming to rest. The coefficient of dynamic friction between the sledge and the snow in this region is . Draw a free-body diagram showing the forces acting on the sledge while it is moving horizontally.
Determine an expression for the distance in terms of , and .
This question is about the motion of a bicycle. A cyclist is moving up a slope that is at an angle of 19° to the horizontal. The mass of the cyclist and the bicycle is 85 kg.
Calculate the component of the weight of the cyclist and bicycle parallel to the slope.
Calculate the normal reaction force on the bicycle from the slope.
At the bottom of the slope the cyclist has a speed of 5.5 m s⁻¹. The cyclist stops pedalling and applies the brakes which provide an additional decelerating force of 250 N. Determine the distance taken for the cyclist to stop. Assume air resistance is negligible and that there are no other frictional forces.
The work done by the centripetal force on an object that moves in a circle at a constant speed is
A force acts on a box of mass 10 kg. The graph below shows how the acceleration of the box varies with its displacement .
What is the work done by the force on the box?
Which quantity has the fundamental SI units of ?
A constant force is applied to a ball of mass . The velocity of the ball changes from to . The impulse received by the ball is
A comet of mass is moving with velocity in deep space. It breaks into two pieces: one of mass and the other . If the smaller piece moves away at relative to the original direction, what is the velocity of the larger piece relative to the original direction?
A rocket in deep space expels of fuel at relative to the rocket. What is the speed gained by the rocket as a result of this ejection?
This question is about finding the force that acts upon a car when it is in a head on collision. 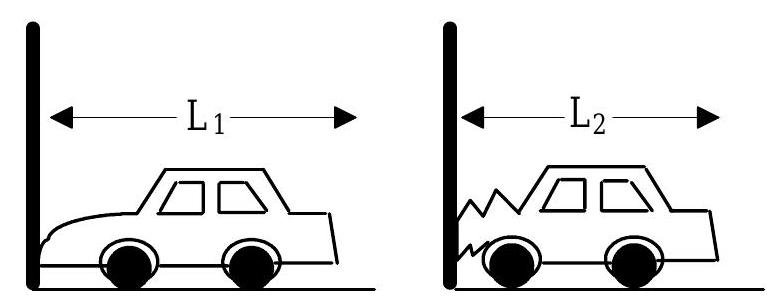 In order to measure collision forces a car is crashed head-on into a flat, rigid barrier and the resulting crush distance is measured. The crush distance is the amount that the car collapses in coming to rest. In the above diagram the crush distance .
In order to measure collision forces a car is crashed head-on into a flat, rigid barrier and the resulting crush distance is measured. The crush distance is the amount that the car collapses in coming to rest. In the above diagram the crush distance .
Show that the average crush force exerted on a car of mass with impact speed is equal to .
The table below gives values of the crush distance, , for different impact speeds , of cars of the same make. (Uncertainties in measurement are not given.)
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 3.0 | 0.08 | .......... |
| 10.0 | 0.35 | .......... |
| 15.0 | 0.65 | .......... |
| 20.0 | 1.02 | .......... |
Complete the last column of the table.
Plot a graph of against .
Consider the situation in which a car of mass has an impact speed of . Use information from the graph you have drawn to find the average force exerted on the car during the collision as it is brought to rest.
Calculate the time it takes this car to come to rest from the moment of impact.