- IB
- Reactivity 3. What are the mechanisms of chemical change?
Practice Reactivity 3. What are the mechanisms of chemical change? with authentic IB Chemistry exam questions for both SL and HL students. This question bank mirrors Paper 1A, 1B, 2 structure, covering key topics like atomic structure, chemical reactions, and organic chemistry. Get instant solutions, detailed explanations, and build exam confidence with questions in the style of IB examiners.
The iron(III) ion forms the complex ion shown.
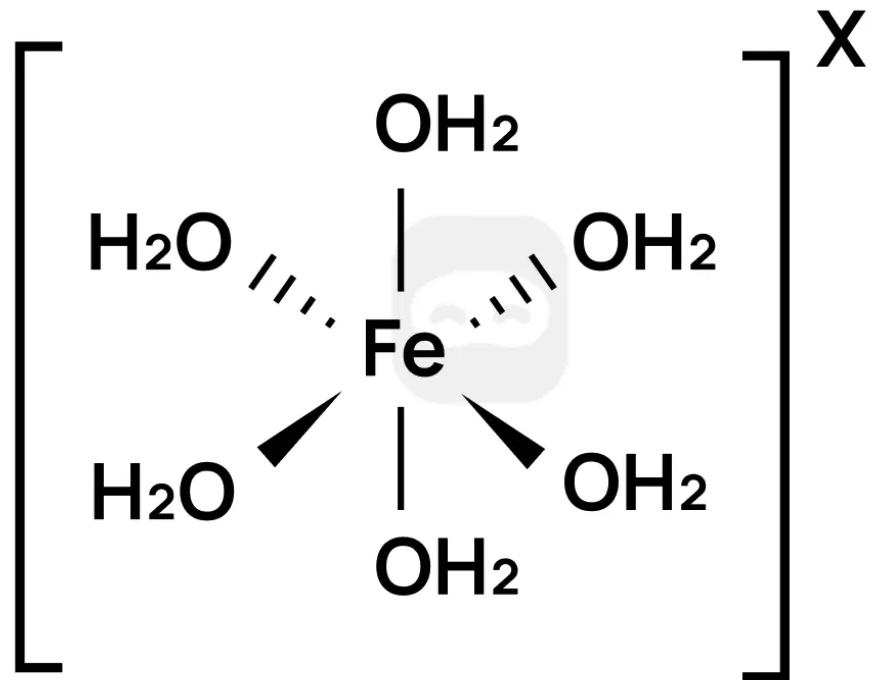
Which statements are correct?
I. The charge on the complex ion is 3+
II. The water molecules are acting as Lewis bases
III. The complex ion forms a coloured solution
Which of the following is not a nucleophile?
The apparatus for the electrolysis of molten sodium chloride is shown.
Which statement is correct?
Which of the following is always true in a redox reaction?
The acid-base indicator phenol red, , changes colour from yellow to red over a pH range of --. Which statement is correct?
Which compound can be oxidised when heated with an acidified solution of potassium dichromate(VI)?
Which combination of acid and base is most likely to have a pH of 8.5 at the equivalence point in a titration?
What is the major product of the reaction between and but-2-ene?
Which statement is correct?
What are the products of electrolysis when concentrated calcium bromide solution is electrolysed using graphite electrodes?
| Product at cathode (negative electrode) | Product at anode (positive electrode) | |
|---|---|---|
| A. | hydrogen | bromine |
| B. | calcium | oxygen |
| C. | calcium | bromine |
| D. | hydrogen | oxygen |