Practice B1.1 Carbohydrates and lipids with authentic IB Biology exam questions for both SL and HL students. This question bank mirrors Paper 1A, 1B, 2 structure, covering key topics like cell biology, genetics, and ecology. Get instant solutions, detailed explanations, and build exam confidence with questions in the style of IB examiners.
During digestion, how is a water molecule used to break down polymers into monomers?
What feature of cellulose allows it to form rigid plant cell walls?
What characteristic of glucose makes it suitable for transport in the bloodstream?
Which of the following is an organic compound?
The diagrams show how monosaccharide molecules are joined to form chains in two polysaccharides.
Using the diagram and the table, which diagram and monosaccharide represent glycogen?
| Diagram | Monosaccharide that makes up the chain | |
|---|---|---|
| A. | A | glucose |
| B. | A | maltose |
| C. | B | glucose |
| D. | B | maltose |
The diagram shows an image of a plant cell, which type of carbohydrate provides structural support in plant cell walls?
How is carbon able to form a wide variety of stable organic molecules?
What makes starch suitable for energy storage in plant cells?
| Property | Contribution to Storage Function | |
|---|---|---|
| I | Insolubility in water | Prevents osmotic imbalance |
| II | Helical structure | Enables compact packing |
| III | Easily hydrolyzed | Allows rapid energy release |
What is a reason glycogen offers a metabolic advantage over unbranched polysaccharides?
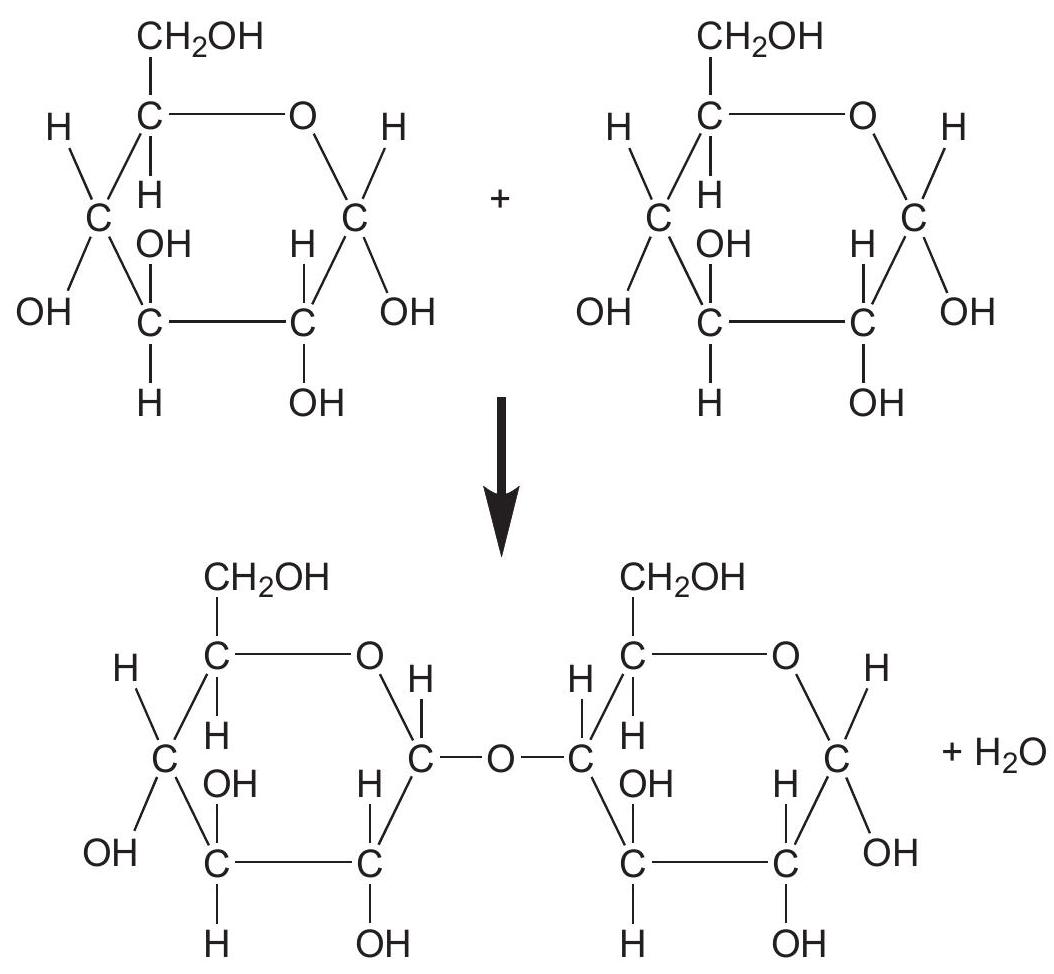
What type of molecule is formed by the chemical reaction shown in the diagram?