Practice B.4 Thermodynamics (HL only) with authentic IB Physics exam questions for both SL and HL students. This question bank mirrors Paper 1A, 1B, 2 structure, covering key topics like mechanics, thermodynamics, and waves. Get instant solutions, detailed explanations, and build exam confidence with questions in the style of IB examiners.
Which statement is a consequence of the second law of thermodynamics in terms of statistical mechanics?
Which expression defines entropy change for a reversible process?
An ideal monatomic gas expands adiabatically from volume to . If its initial temperature is , what is its final temperature?
The diagram below represents an ideal and monatomic gas that first undergoes a compression, followed by an increase in pressure.
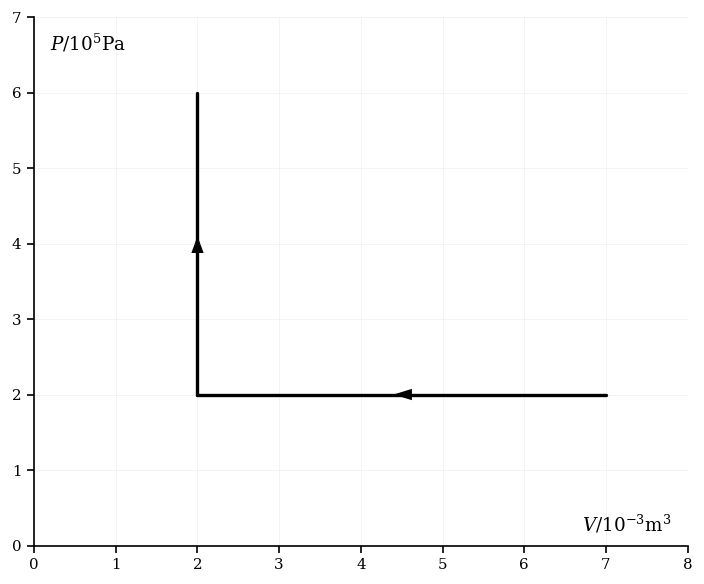
Calculate the work done during the compression.
Calculate the work done during the increase in pressure.
An adiabatic process then increases the volume of the gas to . Calculate the pressure following this process.
Outline how you can achieve an approximate adiabatic change in practice.
A gas expands adiabatically. A student records its pressure and volume and plots the graph below:
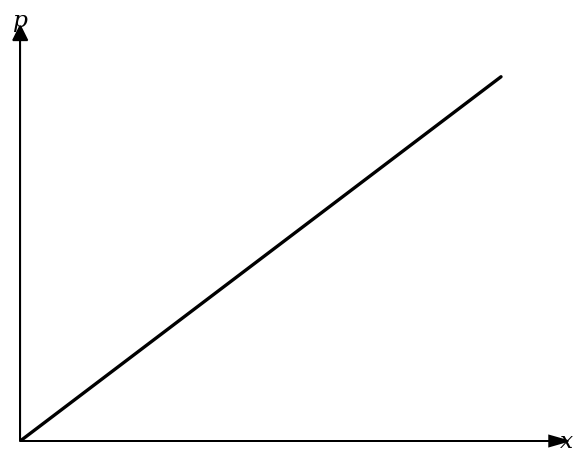
What is the most likely quantity on the x-axis?
A working refrigerator with the door open is placed in a sealed room. The entropy of the room:
Which of the following processes can be represented as a vertical line on a diagram for an ideal gas?
Which of the following is true when thermal energy is converted into work in a single process and a cyclical process?
| Single process | Cyclical process | |
|---|---|---|
| A. | complete conversion of thermal energy into work can occur | energy must be transferred from the system |
| B. | complete conversion of thermal energy into work can never occur | energy must be transferred from the system |
| C. | complete conversion of thermal energy into work can occur | energy need not be transferred from the system |
| D. | complete conversion of thermal energy into work can never occur | energy need not be transferred from the system |
The fraction of the internal energy that is due to molecular vibration varies in the different states of matter. What gives the order from highest fraction to lowest fraction of internal energy due to molecular vibration?
The entropy of a system